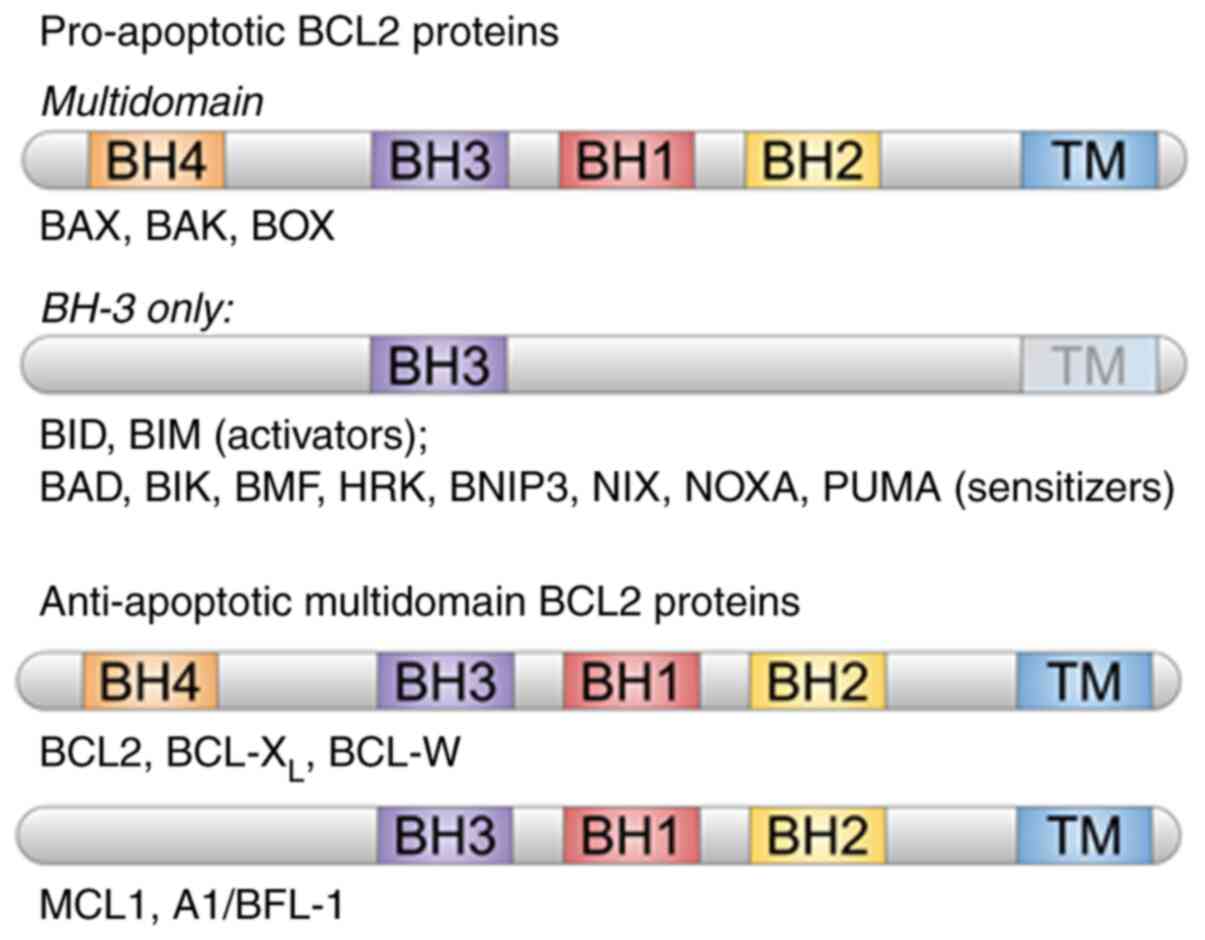
Molecular Imaging of Apoptosis in Atherosclerosis by Targeting Cell Membrane Phospholipid Asymmetry - ScienceDirect
Detection of apoptosis in patients with coronary artery disease Assessment of temporal patterns and potential sources

Dickkopf1 destabilizes atherosclerotic plaques and promotes plaque formation by inducing apoptosis of endothelial cells through activation of ER stress | Cell Death & Disease

Drug‐Eluting Stent Targeting Sp‐1‐Attenuated Restenosis by Engaging YAP‐Mediated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation | Journal of the American Heart Association

Anagliptin prevents apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by modulating NOX-4 signaling pathways - ScienceDirect

Combination of microRNA-21 and microRNA-146a Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction and Apoptosis During Acute Myocardial Infarction in Mice: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids

A Senolytic-Eluting Coronary Stent for the Prevention of In-Stent Restenosis | ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering

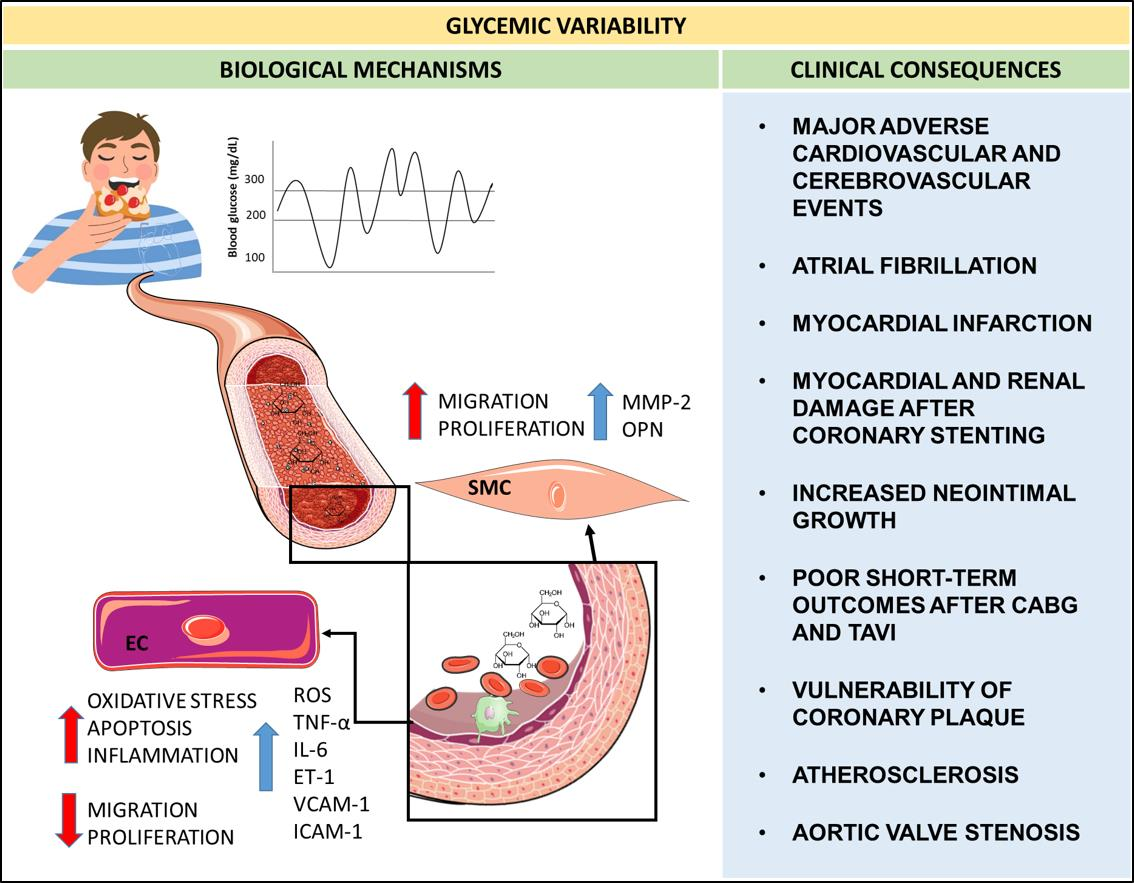
Hyperglycaemia‐associated Caspase‐3 predicts diabetes and coronary artery disease events - Sun - 2021 - Journal of Internal Medicine - Wiley Online Library

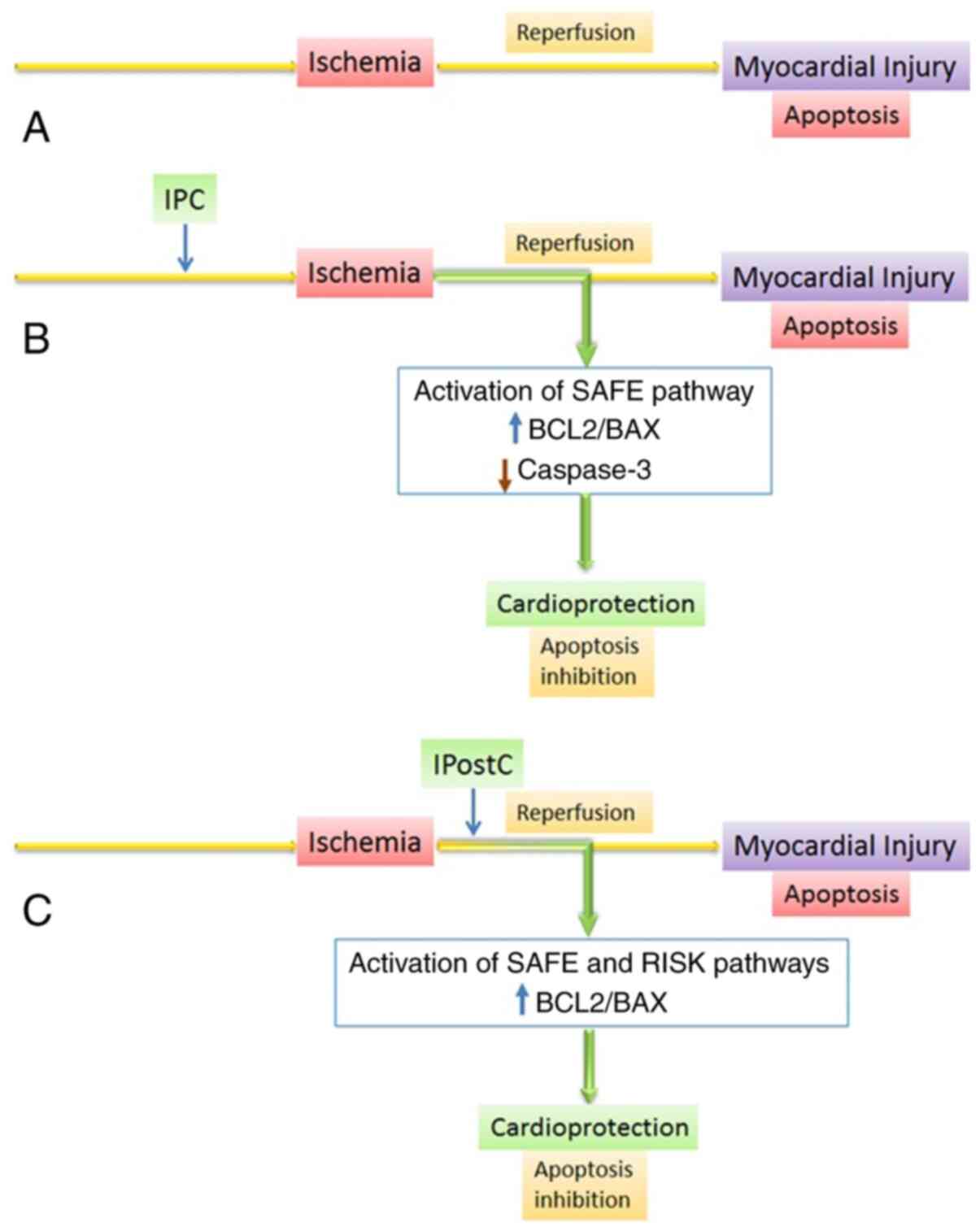
Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease - Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology
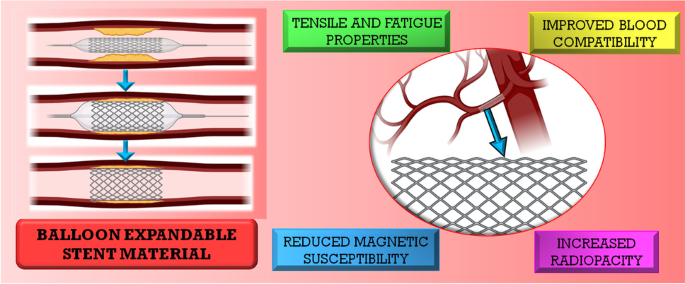
Balloon expandable coronary stent materials: a systematic review focused on clinical success | SpringerLink

Development of Dual Drug Eluting Cardiovascular Stent with Ultrathin Flexible Poly(l-lactide-co-caprolactone) Coating | ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering

Bioengineering | Free Full-Text | Understanding the Impact of Stent and Scaffold Material and Strut Design on Coronary Artery Thrombosis from the Basic and Clinical Points of View
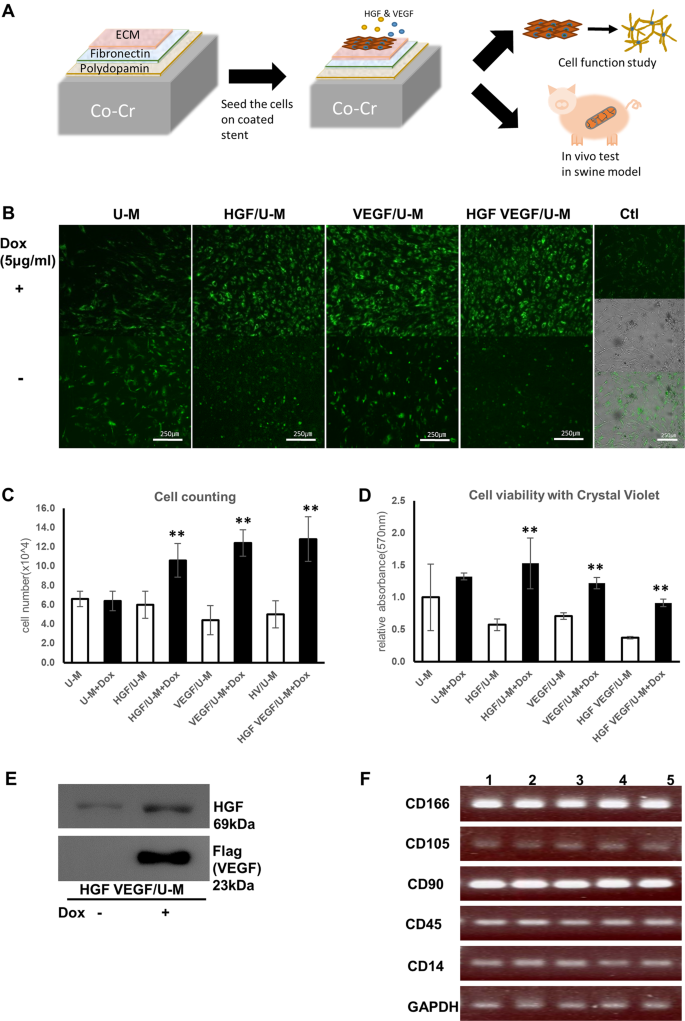
Coronary stents with inducible VEGF/HGF-secreting UCB-MSCs reduced restenosis and increased re-endothelialization in a swine model | Experimental & Molecular Medicine
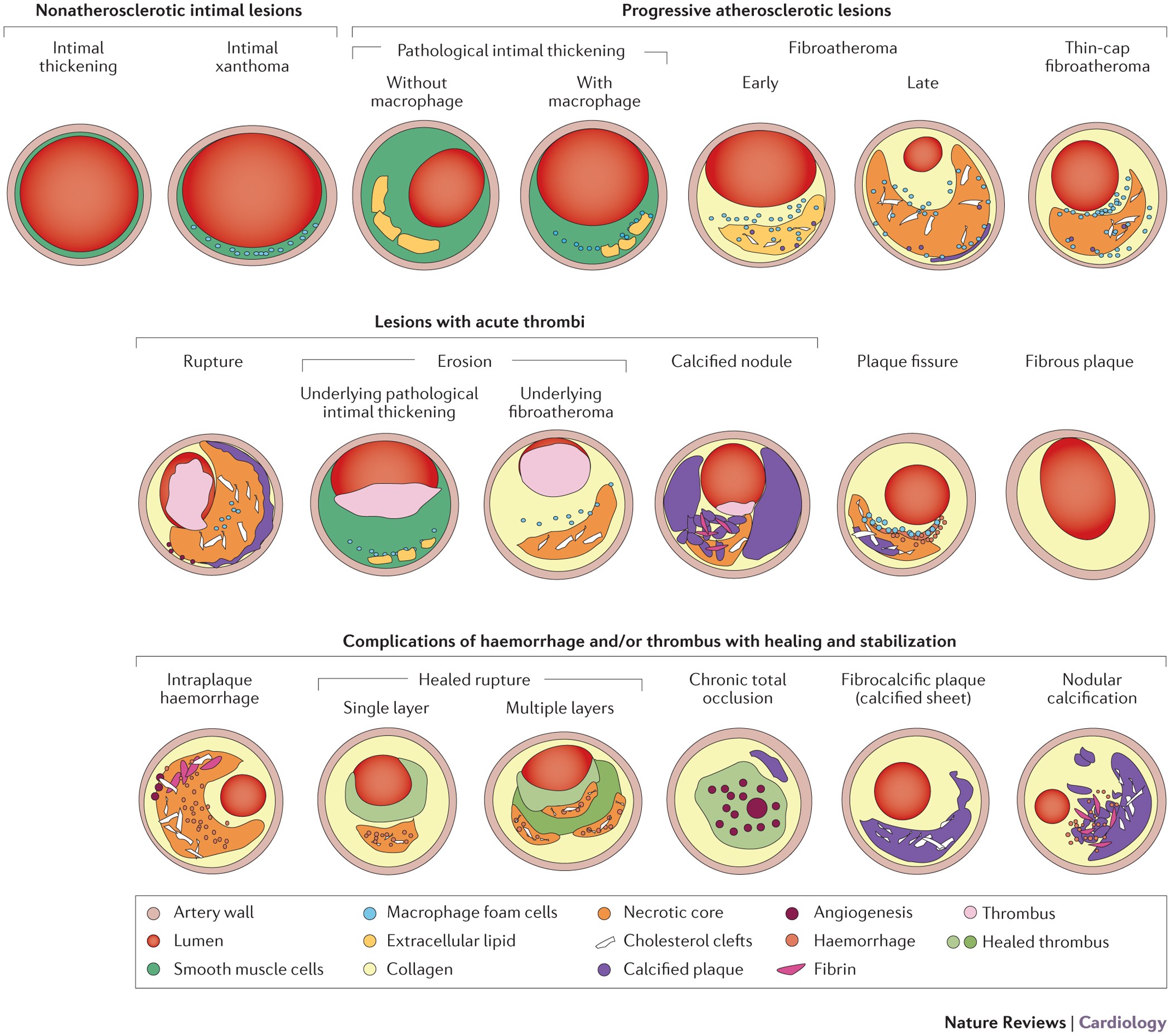
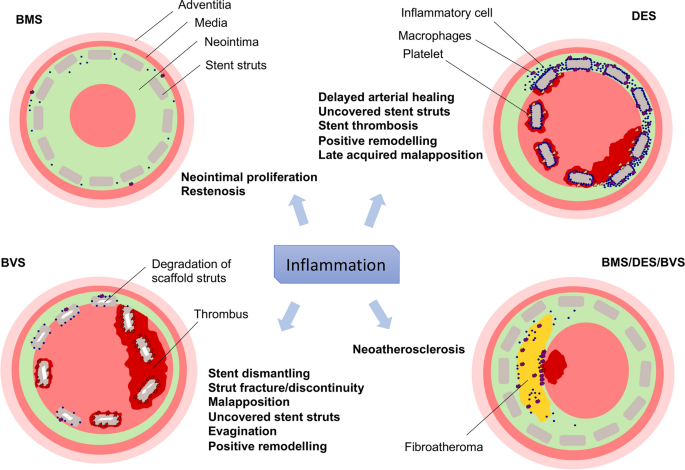
Pathophysiology of native coronary, vein graft, and in-stent atherosclerosis | Nature Reviews Cardiology

Future strategies in the diagnosis of patients with coronary artery disease – are we stenting the wrong coronary artery lesions? | Future Cardiology

Life | Free Full-Text | In Stent Neo-Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Implications, Prevention, and Therapeutic Approaches
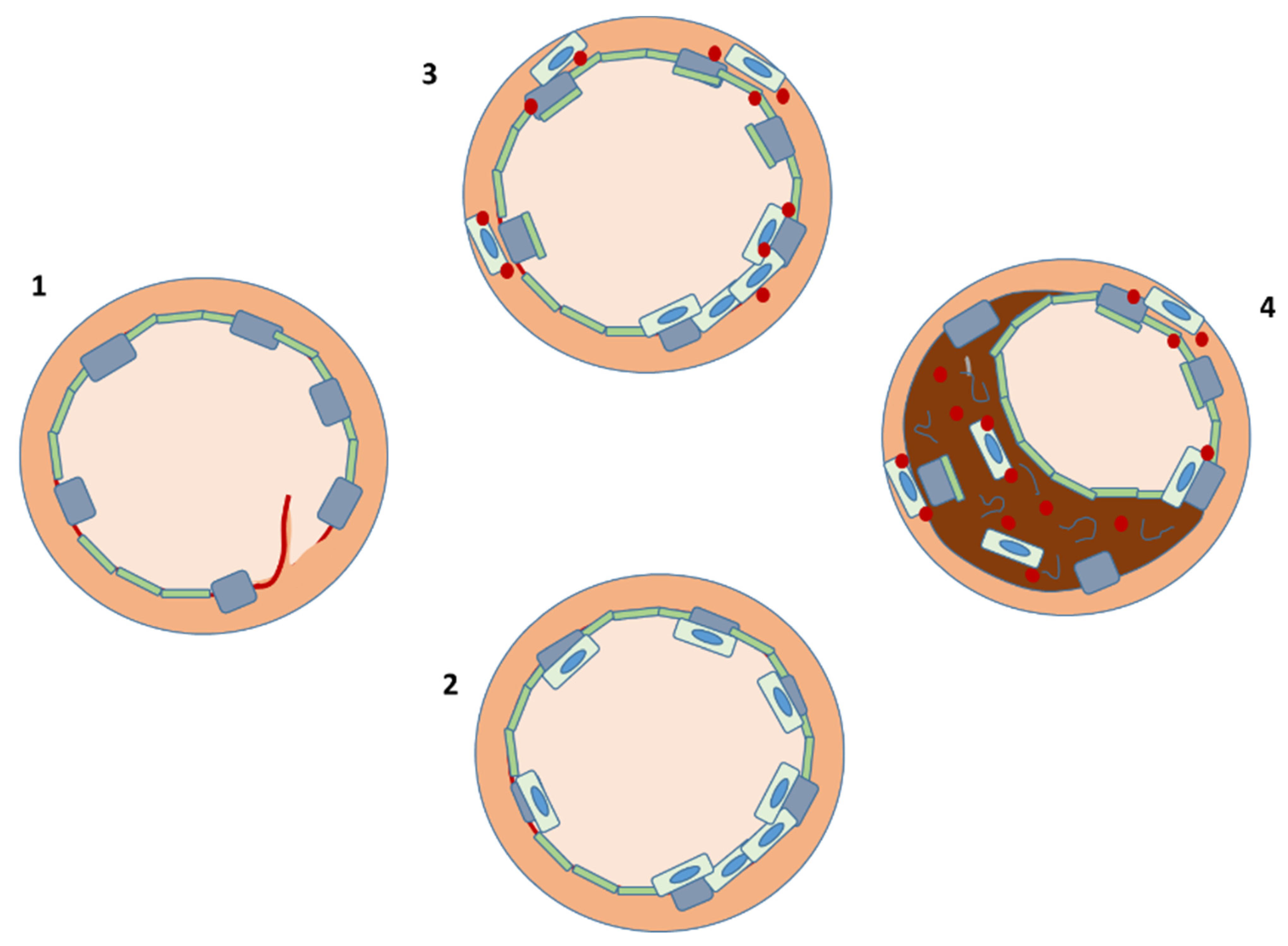
Cells | Free Full-Text | Restenosis after Coronary Stent Implantation: Cellular Mechanisms and Potential of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (A Short Guide for the Interventional Cardiologist)
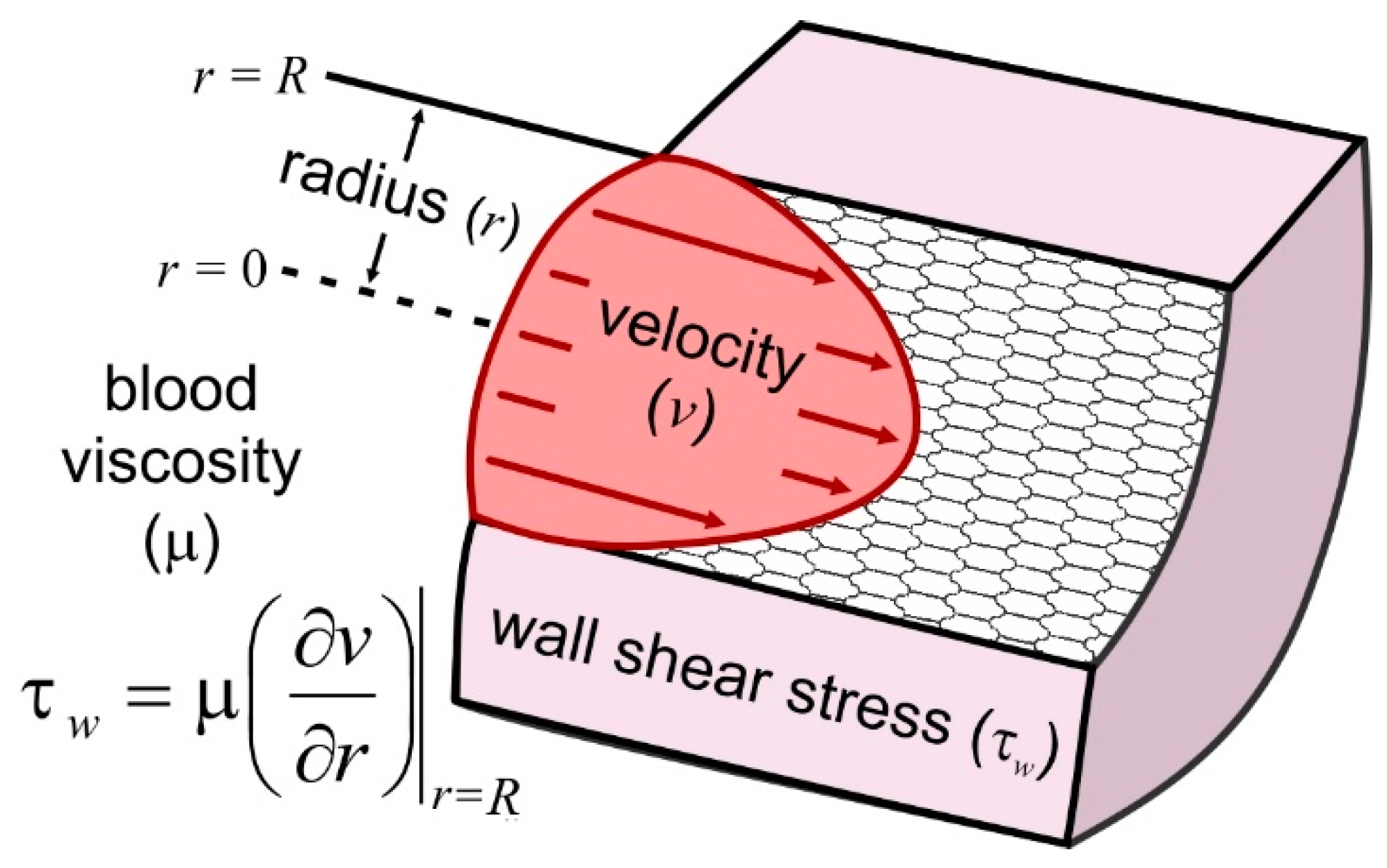
Fluids | Free Full-Text | Advancements and Opportunities in Characterizing Patient-Specific Wall Shear Stress Imposed by Coronary Artery Stenting
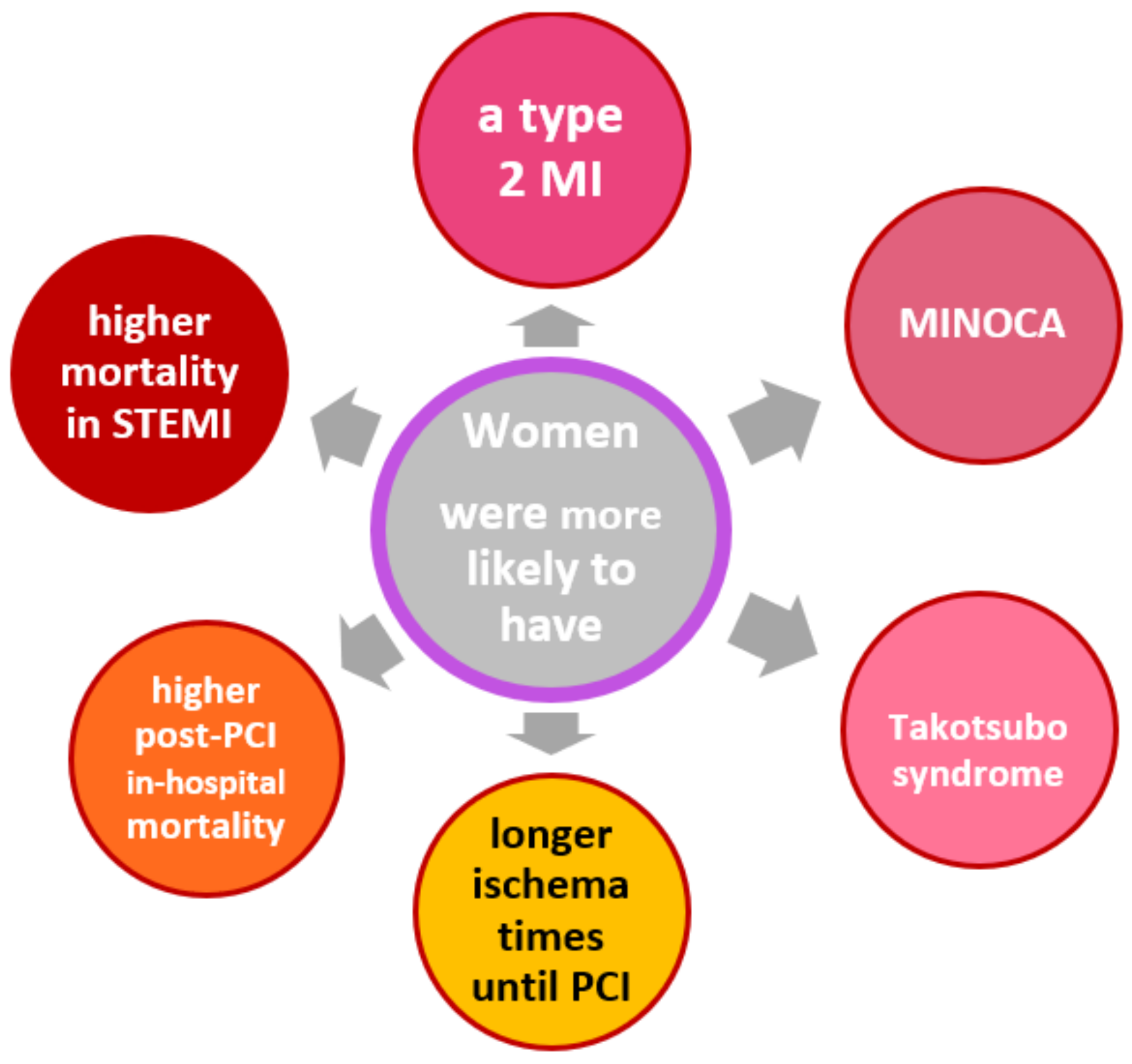
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Coronary Artery Disease and Cancer: Treatment and Prognosis Regarding Gender Differences

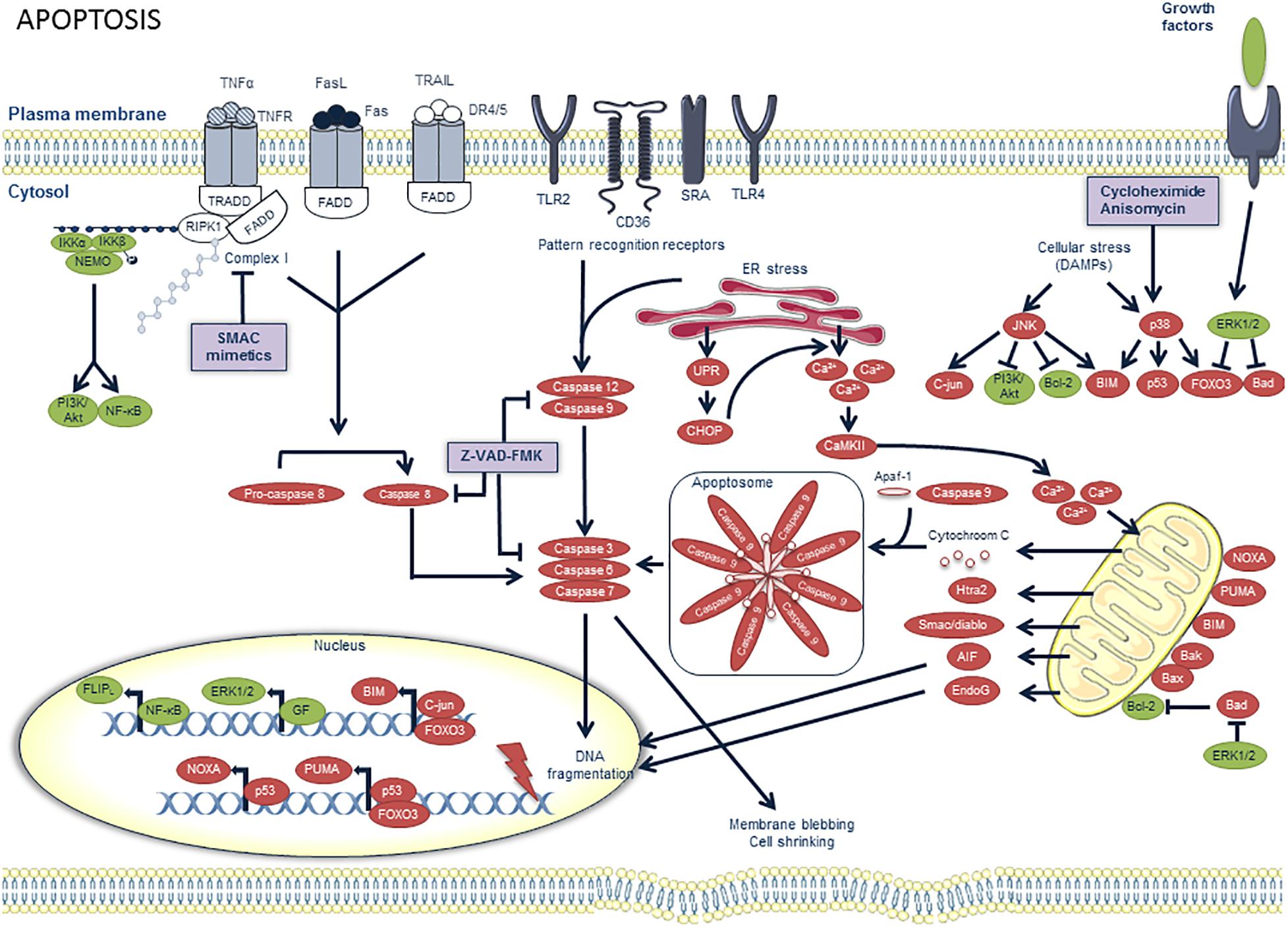
Fundamental Mechanisms of Regulated Cell Death and Implications for Heart Disease | Physiological Reviews